Priority Queues are used to short heaps. Priority queues are used in operating system for load balancing and interrupt handling. Priority queues are used in huffman codes for data compression. In traffic light, depending upon the traffic, the colors will be given priority.
Difference b/w priority queue and normal queue:
In a queue, the first-in-first-out rule is implemented whereas, in a priority queue, the values are removed on the basis of priority. The element with the highest priority is removed first.
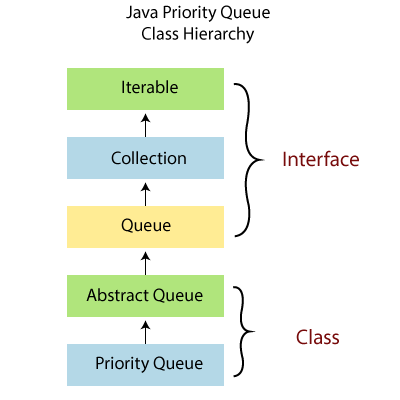
Implementation of Priority queue:
public class PriorityQueueEx {
PriorityQueue intQueue = new PriorityQueue();
PriorityQueueEx() {
intQueue.add(10);
intQueue.add(5);
intQueue.add(15);
System.out.println(intQueue);
System.out.println("Peek " + intQueue.peek());
System.out.println("Poll " + intQueue.poll());
System.out.println(intQueue);
}
public static void main(String strp[]) {
PriorityQueueEx queueEx = new PriorityQueueEx();
}
}
Output:
[5, 10, 15]Peek 5Poll 5[10, 15]PriorityQueue.poll() method is used to retrieve or fetch and remove the first element of the Queue or the element present at the head of the Queue. The peek() method only retrieved the element at the head but the poll() also removes the element along with the retrieval. It returns NULL if the queue is empty.
The remove() and poll() methods differ only in their behavior when the queue is empty: the remove() method throws an exception, while the poll() method returns null. The element() and peek() methods return, but do not remove, the head of the queue.






Leave a comment