- Arrays
- Stacks
- Queues
- Linked Lists
- Trees
- Graphs
- Hash-table
Arrays:
An array is the simplest and most widely used data structure. Other data structures like stacks and queues are derived from arrays.
Here’s an image of a simple array of size 4, containing elements (1, 2, 3 and 4).
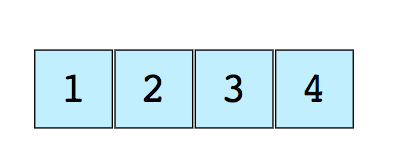
The following are the two types of arrays:
- One-dimensional arrays (as shown above)
- Multi-dimensional arrays (arrays within arrays)
Basic Operations on Arrays
- Insert — Inserts an element at given index
- Get — Returns the element at given index
- Delete — Deletes an element at given index
- Size — Get the total number of elements in array
Commonly asked Array interview questions
- Find the second minimum element of an array
- First non-repeating integers in an array
- Merge two sorted arrays
- Rearrange positive and negative values in an array
Stacks:
A real-life example of Stack could be a pile of books placed in a vertical order. In order to get the book that’s somewhere in the middle, you will need to remove all the books placed on top of it. This is how the LIFO (Last In First Out) method works.
Here’s an image of stack containing three data elements (1, 2 and 3), where 3 is at the top and will be removed first:
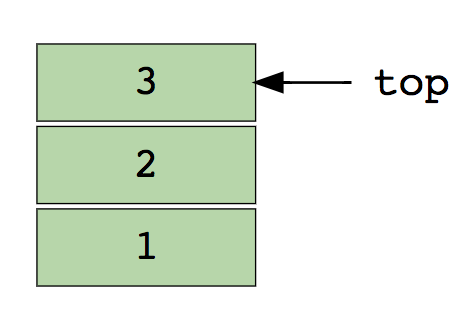
Basic operations of stack
- Push — Inserts an element at the top
- Pop — Returns the top element after removing from the stack
- isEmpty — Returns true if the stack is empty
- Top — Returns the top element without removing from the stack
Commonly asked Stack interview questions
- Evaluate postfix expression using a stack
- Sort values in a stack
- Check balanced parentheses in an expression
Queues:
Similar to Stack, Queue is another linear data structure that stores the element in a sequential manner. The only significant difference between Stack and Queue is that instead of using the LIFO method, Queue implements the FIFO method, which is short for First in First Out.
Here’s an image of Queue containing four data elements (1, 2, 3 and 4), where 1 is at the top and will be removed first:
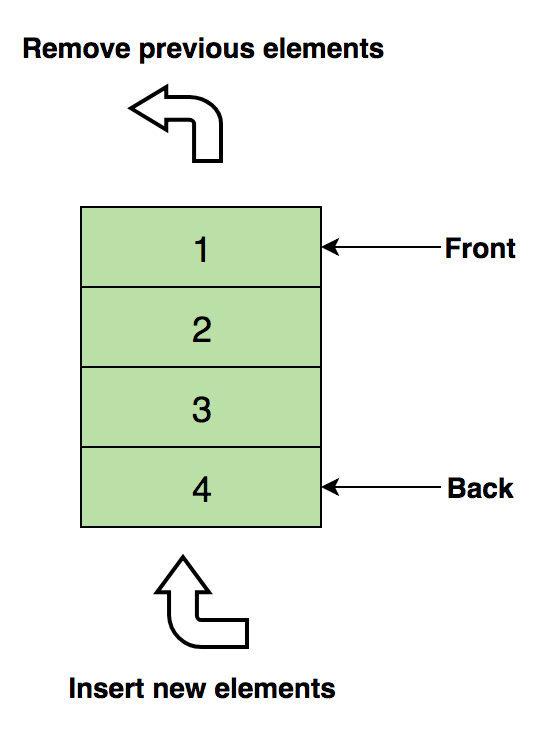
Basic operations of Queue
- Enqueue() — Inserts element to the end of the queue
- Dequeue() — Removes an element from the start of the queue
- isEmpty() — Returns true if queue is empty
- Top() — Returns the first element of the queue
Commonly asked Queue interview questions
- Implement stack using a queue
- Reverse first k elements of a queue
- Generate binary numbers from 1 to n using a queue
Linked Lists:
A linked list is another important linear data structure which might look similar to arrays at first but differs in memory allocation, internal structure and how basic operations of insertion and deletion are carried out.
A linked list is like a chain of nodes, where each node contains information like data and a pointer to the succeeding node in the chain. There’s a head pointer, which points to the first element of the linked list, and if the list is empty then it simply points to null or nothing.
Linked lists are used to implement file systems, hash tables, and adjacency lists.
Here’s a visual representation of the internal structure of a linked list:

Following are the types of linked lists:
- Singly Linked List (Unidirectional)
- Doubly Linked List (Bi-directional)
Basic operations of Linked List:
- InsertAtEnd — Inserts given element at the end of the linked list
- InsertAtHead — Inserts given element at the start/head of the linked list
- Delete — Deletes given element from the linked list
- DeleteAtHead — Deletes first element of the linked list
- Search — Returns the given element from a linked list
- isEmpty — Returns true if the linked list is empty
Commonly asked Linked List interview questions
- Reverse a linked list
- Detect loop in a linked list
- Return Nth node from the end in a linked list
- Remove duplicates from a linked list
Graph:
A graph is a set of nodes that are connected to each other in the form of a network. Nodes are also called vertices. A pair(x,y) is called an edge, which indicates that vertex x is connected to vertex y. An edge may contain weight/cost, showing how much cost is required to traverse from vertex x to y.
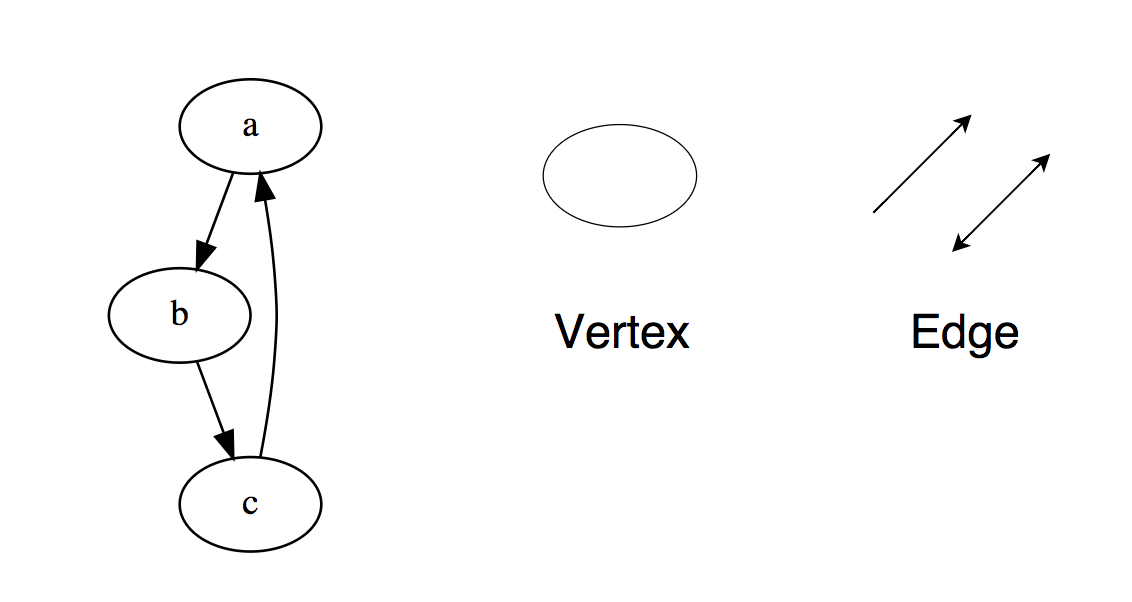
Types of Graphs:
- Undirected Graph
- Directed Graph
In a programming language, graphs can be represented using two forms:
- Adjacency Matrix
- Adjacency List
Common graph traversing algorithms:
- Breadth First Search
- Depth First Search
Commonly asked Graph interview questions:
- Implement Breadth and Depth First Search
- Check if a graph is a tree or not
- Count number of edges in a graph
- Find the shortest path between two vertices
Trees:
A tree is a hierarchical data structure consisting of vertices (nodes) and edges that connect them. Trees are similar to graphs, but the key point that differentiates a tree from the graph is that a cycle cannot exist in a tree.
Trees are extensively used in Artificial Intelligence and complex algorithms to provide an efficient storage mechanism for problem-solving.
Here’s an image of a simple tree, and basic terminologies used in tree data structure:

The following are the types of trees:
- N-ary Tree
- Balanced Tree
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- AVL Tree
- Red Black Tree
- 2–3 Tree
Out of the above, Binary Tree and Binary Search Tree are the most commonly used trees.
Commonly asked Tree interview questions
- Find the height of a binary tree
- Find kth maximum value in a binary search tree
- Find nodes at “k” distance from the root
- Find ancestors of a given node in a binary tree
HashTable/Map:
Hashing is a process used to uniquely identify objects and store each object at some pre-calculated unique index called its “key.” So, the object is stored in the form of a “key-value” pair collection. Each object can be searched using that key. There are different data structures based on hashing, but the most commonly used data structure is the hash table.
Hash tables are generally implemented using arrays.
The performance of hashing data structure depends upon these three factors:
- Hash Function
- Size of the Hash Table
- Collision Handling Method
Here’s an illustration of how the hash is mapped in an array. The index of this array is calculated through a Hash function.
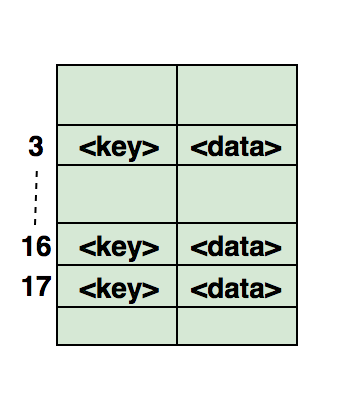
Commonly asked Hashing interview questions
- Find symmetric pairs in an array
- Trace complete path of a journey
- Find if an array is a subset of another array
- Check if given arrays are disjoint





Leave a comment