Docker is an open source containerization platform. It enables developers to package the applications into containers—standardised executable components combining application source code with the operating system (OS) libraries and dependencies required to run that code in any environment.
- Docker Installation
- Docker Container
- Docker Image
- Docker Networking
- Docker Volume
- Docker Compose
- Docker Orchestration
- Docker Swarm
- Kubernetes
- Swarm vs K8s
Docker Installation :
Installing on Windows 10 (Pro or Enterprise)
This is the best experience on Windows, but due to OS feature requirements, it only works on the Pro and Enterprise editions of Windows 10 (with latest `update rollups). You need to install “Docker for Windows” from the Docker Store.
With this Edition I recommend using PowerShell for the best CLI experience. See more info in the next few Lectures.
Installing on Windows 7, 8, or 10 Home Edition
Unfortunately, Microsoft’s OS features for Docker and Hyper-V don’t work in these older versions, and “Windows 10 Home” edition doesn’t have Hyper-V, so you’ll need to install the Docker Toolbox, which is a slightly different approach to using Docker with a VirtualBox VM. This means Docker will be running in a Virtual Machine that sits behind the IP of your OS, and uses NAT to access the internet.
NOTE FOR TOOLBOX USERS: For all examples that use http://localhost , you’ll need to replace with http://192.168.99.100
Installing on Mac
You’ll want to install Docker for Mac, which is great. If you’re on an older Mac with less than OSX Yosemite 10.10.3, you’ll need to install the Docker Toolbox instead.
Installing on Linux
Do *not* use your built in default packages like apt/yum install docker.io because those packages are old and not the Official Docker-Built packages.
I prefer to use the Docker’s automated script to add their repository and install all dependencies: curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh but you can also install in a more manual method by following specific instructions on the Docker Store for your distribution, like this one for Ubuntu.
Docker Container Command Line commands :
docker version [OPTIONS]
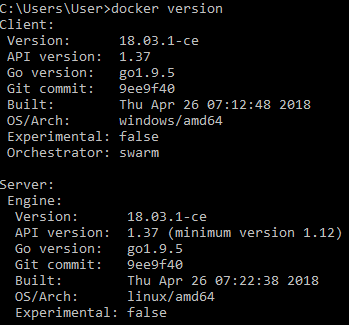
docker info [OPTIONS]

docker container run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
The docker container run is an old command and the new command is docker run. The older command still works in docker.
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]